Exponential Episode 26: DeFi Yield
In this episode of Exponential, Laszlo Szabo, co-founder and CEO of Kiln, joins to talk about one of the most

Welcome to the latest edition of the Nexus Changelog — our regular roundup of technical progress across Nexus OS, CLI, Layer 1, and zkVM.
This cycle focused on smarter task orchestration, better user visibility into proving workflows, and backend enhancements that lay the groundwork for scale.
A key protocol update now enables tasks with multiple input sets and proofs, reducing idle time for nodes and improving concurrency across the network.
On the frontend, users can now track proving progress in real time. Under the hood, parts of the task service were rewritten for performance and reliability, including new logic for task assignment based on node reputation.
Meanwhile, work on the zkVM continued with improvements to constraint efficiency and core circuit optimization.
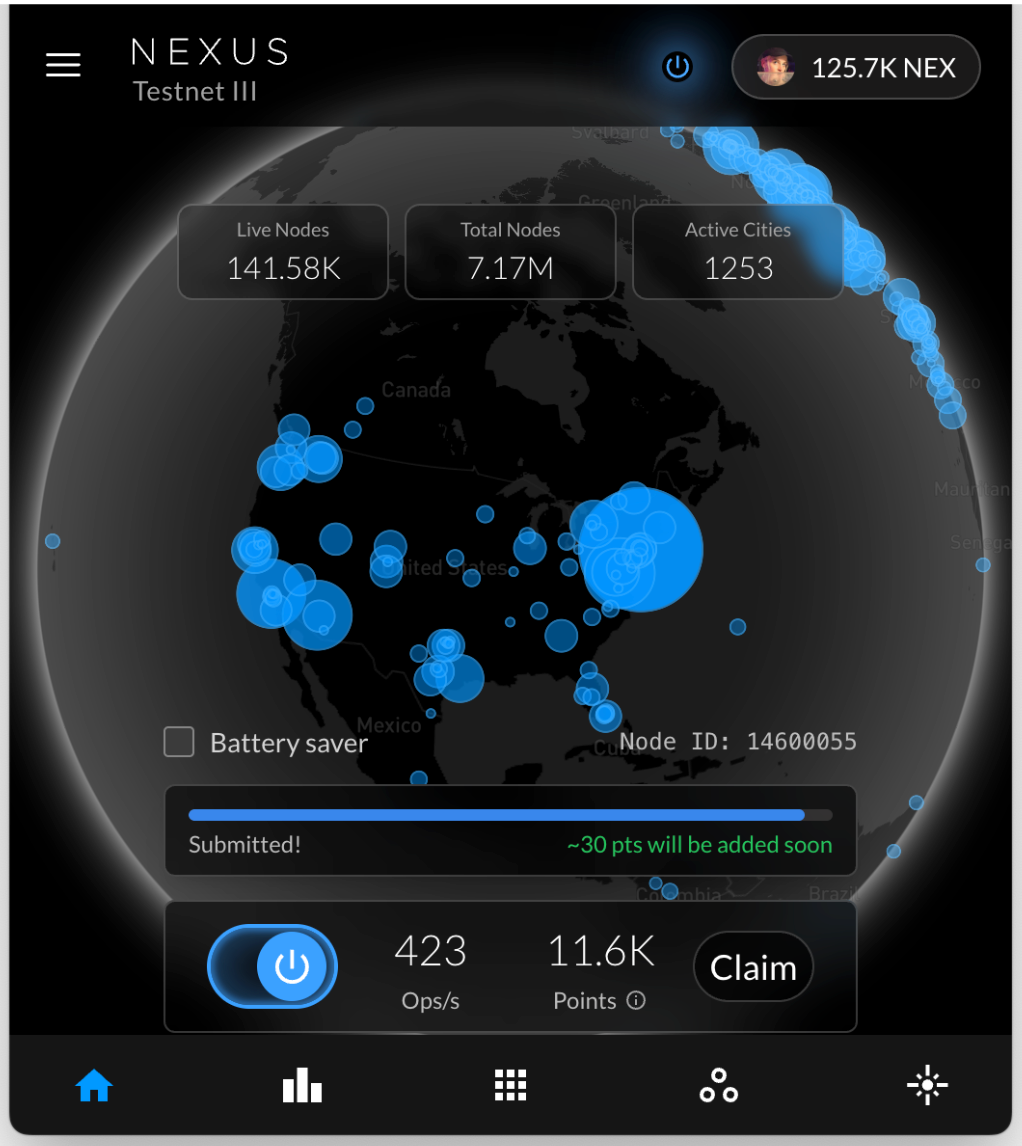
To reduce idle time and improve throughput, we’ve added support for tasks with multiple input sets and proofs. These task structures allow nodes to begin work immediately, even as subsequent inputs are being prepared. As part of this work, the system now provides better visibility into task status and proof submission progress.
The backend continues to evolve with a focus on speed, reliability, and smarter task allocation:
The OS frontend is now equipped with a new proving progress interface, showing granular updates as tasks are processed and proofs are generated. This upgrade helps users monitor their contributions in real time, improving transparency and trust in the proving workflow.
The leaderboard has also been updated with weekly views and date-based filters, making it easier to track top contributors over time. On mobile, layout and font rendering have been refined for better readability across devices.
Finally, request efficiency has been improved by sending only essential authentication data for most calls — a small but meaningful gain in performance, especially for lower-bandwidth users.
The CLI now supports dynamic version reporting, allowing the server to verify client compatibility in real time. This means users will receive tailored upgrade prompts when their build is out of sync, improving network coherence as the protocol evolves.
Work on the zkVM this cycle focused on optimizing the new constraints framework, with changes aimed at improving both proving efficiency and circuit completeness. These updates continue to support the broader effort to modularize and scale the prover architecture.
Together, these updates strengthen every layer of the Nexus stack — from task orchestration to UI clarity to proving speed. As we head toward broader participation and new feature releases, these foundations will support a smoother, more scalable proving experience for all users.
Follow development progress on GitHub or dive deeper in Nexus Docs.